Development of Sustainable Manufacturing Processes for Locally Sourced Materials in Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23960/mech.v16i2.6284Abstract Views: 168 File Views: 126
Keywords:
Energy-Efficient Technologies, Sustainable Construction, Nigeria, Regulatory Support, Stakeholder Awareness, Financial Barriers, Environmental SustainabilityAbstract
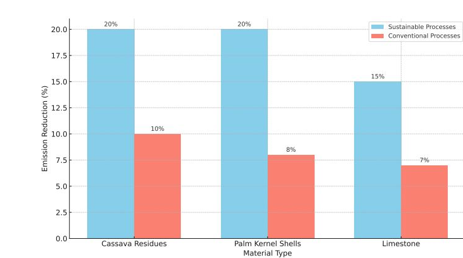
This study explores the development and benefits of sustainable manufacturing processes in Nigeria using locally sourced materials, specifically cassava residues, palm kernel shells, and limestone. Driven by the need to reduce dependency on imported resources, this research addresses economic, environmental, and social impacts associated with conventional manufacturing practices. Results indicate that cassava residues and palm kernel shells demonstrate high compressive and tensile strengths, making them viable alternatives to synthetic materials in structural applications. Limestone, optimized through local sourcing and CO₂ capture technology, proved effective in cement production, reducing carbon emissions by up to 15%. Process optimization, including thermal recovery systems, led to an average energy savings of 25%, while emission reductions across processes averaged 20%. Economic analysis highlighted a 22% reduction in total costs, attributed to savings on transportation and energy, underscoring the financial viability of local resource utilization. The environmental and economic advantages demonstrate sustainable manufacturing’s potential to enhance Nigeria’s resilience to global supply chain disruptions, support local job creation, and align with the country’s climate goals. The study recommends policy support through incentives for sustainable practices, investment in recycling and waste processing infrastructure, and training programs to ensure skilled implementation. Future research should expand these processes to other materials and sectors, integrating advanced monitoring technologies for further efficiencies. These findings provide a foundational approach for Nigeria’s shift towards a sustainable, economically resilient manufacturing sector.
Downloads
References
Ayodele, T., & Nwafor, E. (2020). Sustainable Manufacturing Practices in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Focus on Nigeria. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17(5), 2395–2406.
Smith, J. M., & Banya, O. (2018). Green Manufacturing Processes: An Overview of Global Applications and Case Studies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 174, 947–961.
Muhammad, A. H., & Suleiman, Y. (2021). The Impact of Global Crises on Nigerian Manufacturing Supply Chains. Global Economy Journal, 14(2), 167–179.
Ugochukwu, M. I., & Onukwube, I. J. (2021). Challenges and Opportunities in Nigeria's Manufacturing Sector. Journal of Sustainable Development in Africa, 23(4), 56–67.
United Nations. (2015). Sustainable Development Goals.
Okafor, C. N., & Chukwuneke, F. O. (2019). Environmental Impacts of Non-Sustainable Manufacturing in Nigeria. Environmental Science and Policy, 92, 66–73.
Olorunfemi, I. E., & Akinpelu, M. T. (2022). Assessment of Locally Available Raw Materials for Sustainable
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

MECH is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



